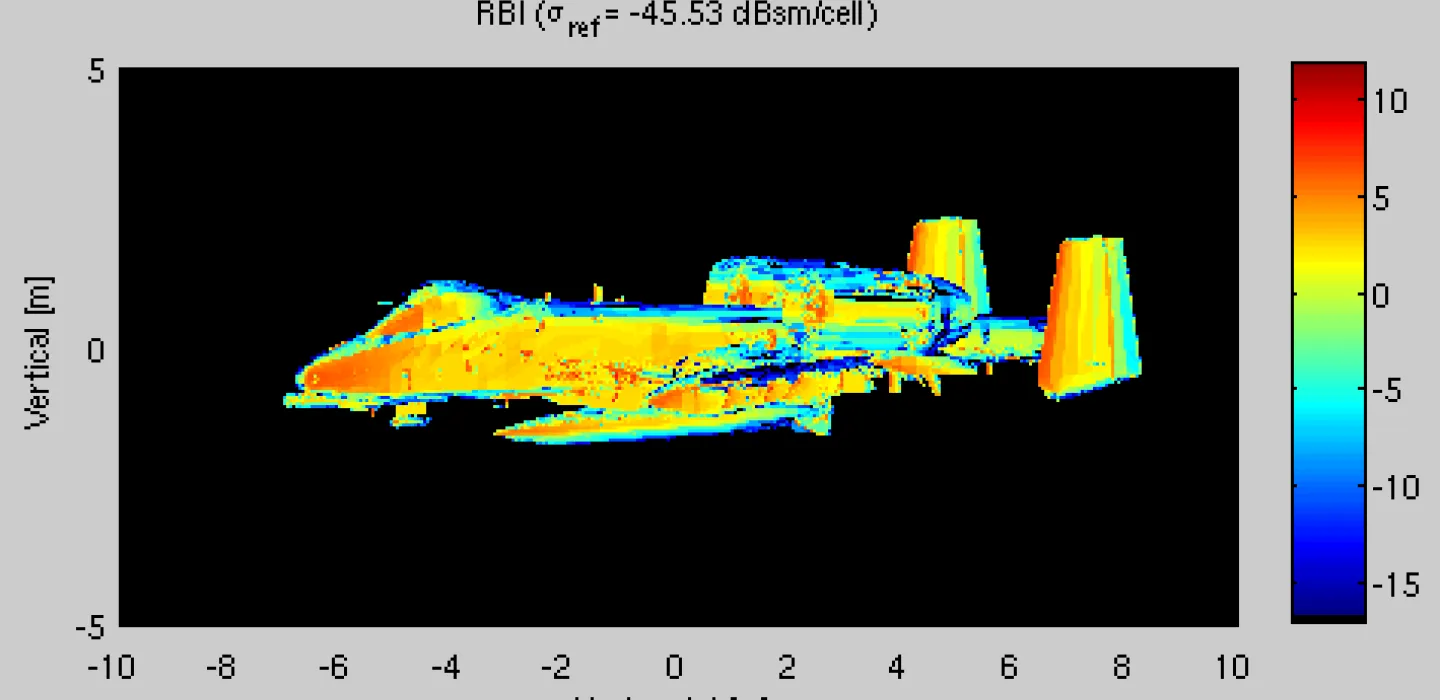
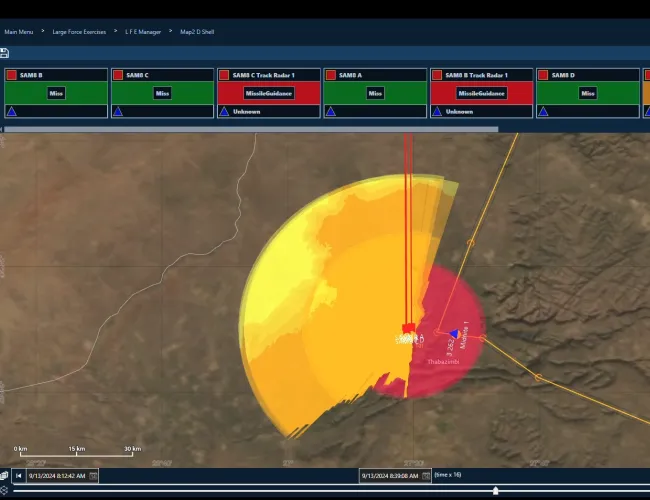
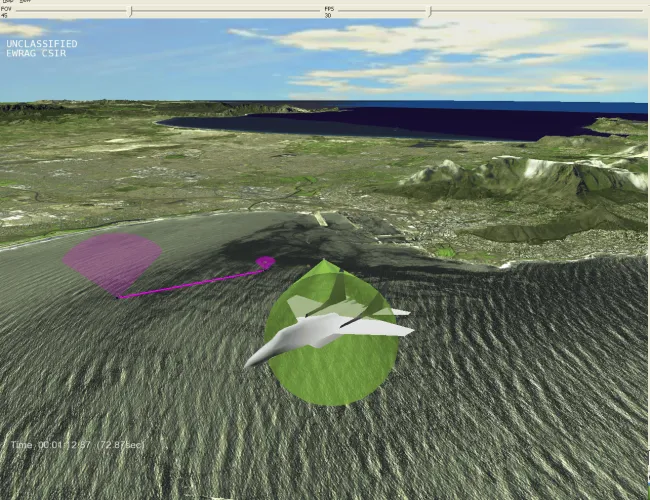
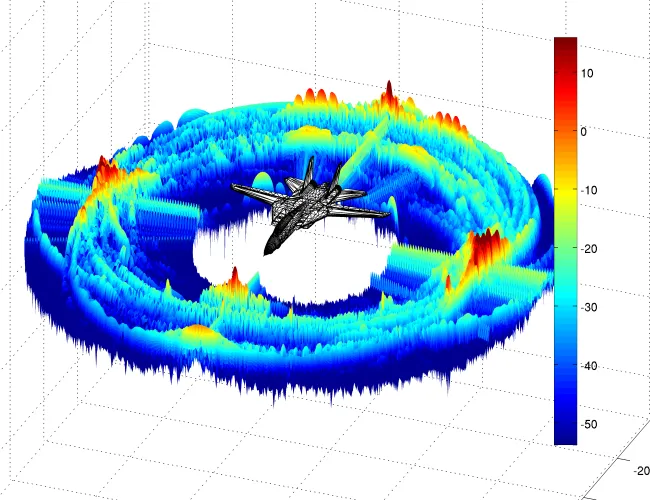
What we do
Contact information:
Highlights
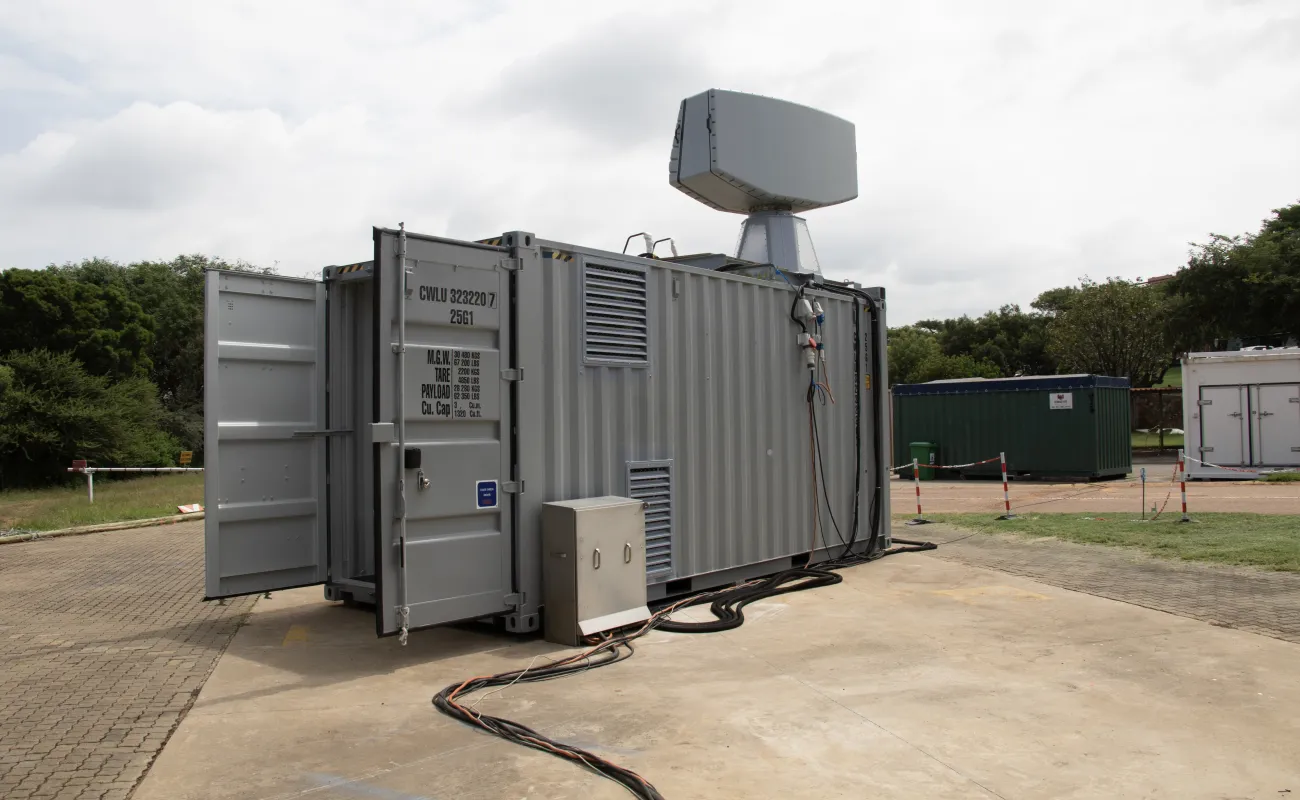

A multi-mission radar for naval, air and surface-surveillance
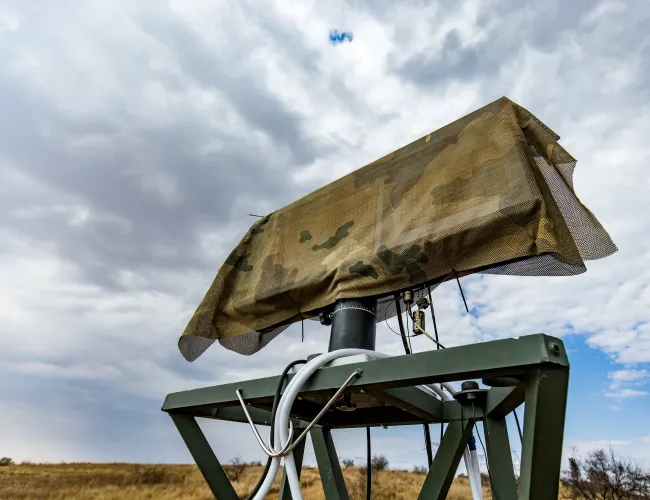
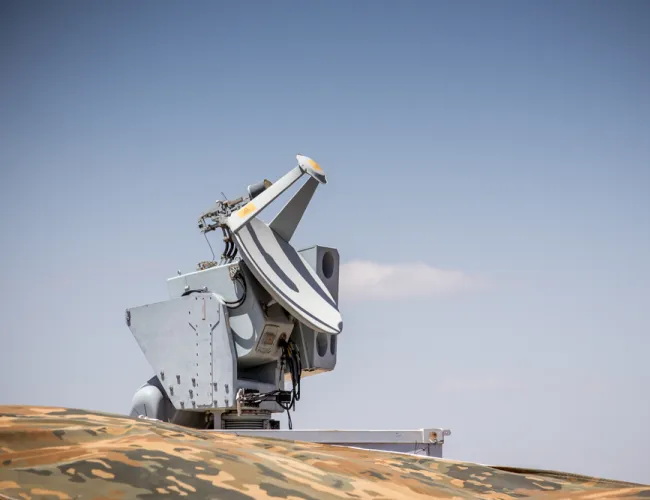
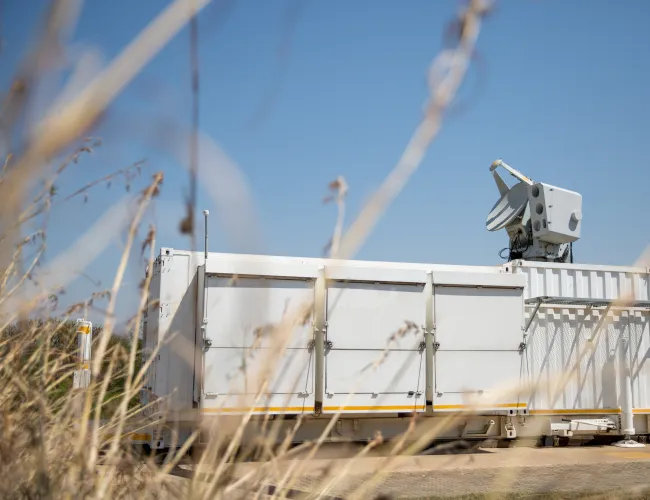
The CSIR and Hensoldt South Africa jointly developed a dual-mode, multi-mission surveillance radar for naval, air and surface surveillance. The Quadome Radar provides naval forces and maritime security authorities with unprecedented situational awareness and rapid response capabilities. Quadome is designed for the global market for tactical naval radar systems, with a focus on offshore patrol vessels, corvettes, light frigates and support vessels. Three Quadome radars have been acquired by the UK Royal Navy.
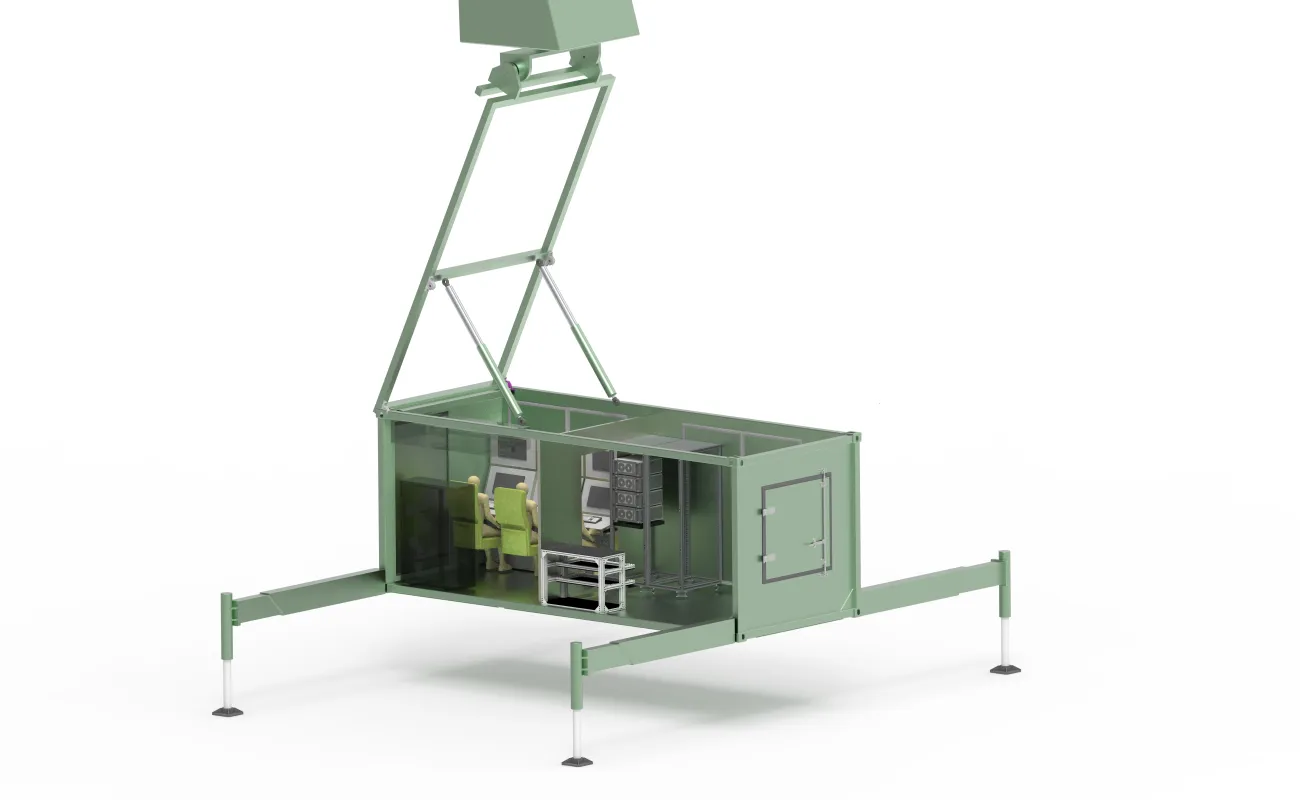

Co-development of next-gen multifunction electronic warfare systems
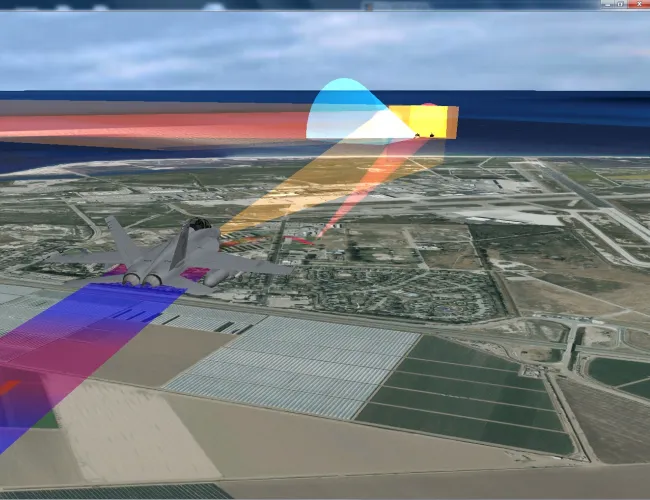
The CSIR, in collaboration with an international partner, is developing an advanced surface-based radar jammer that leverages active electronically scanned array technology and the latest processing innovations, including digital radio frequency memory and heterogeneous computing, for multi-threat engagement. The system is envisioned to be capable of operating across a spectrum of conflict scenarios – from surveillance and counter insurgency in civilian or commercial settings to high-intensity state-on-state conflict.
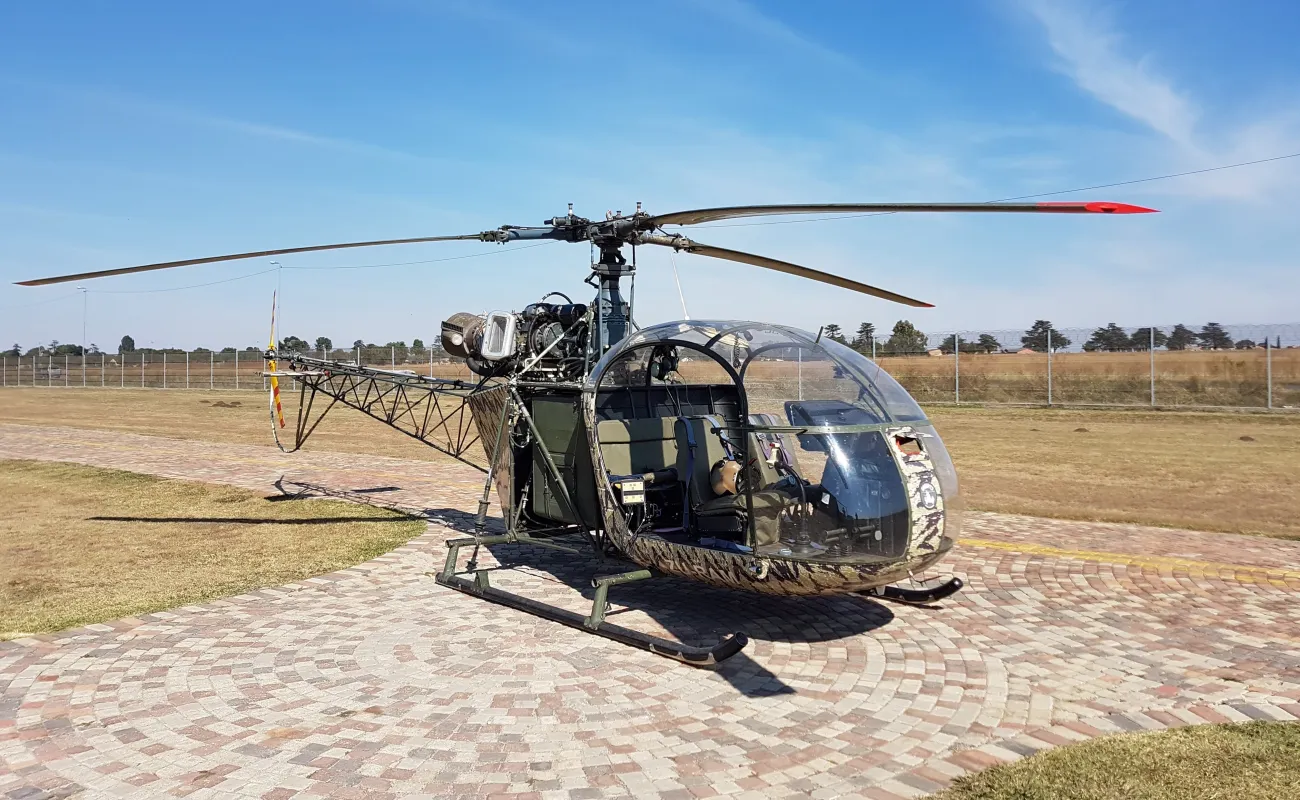

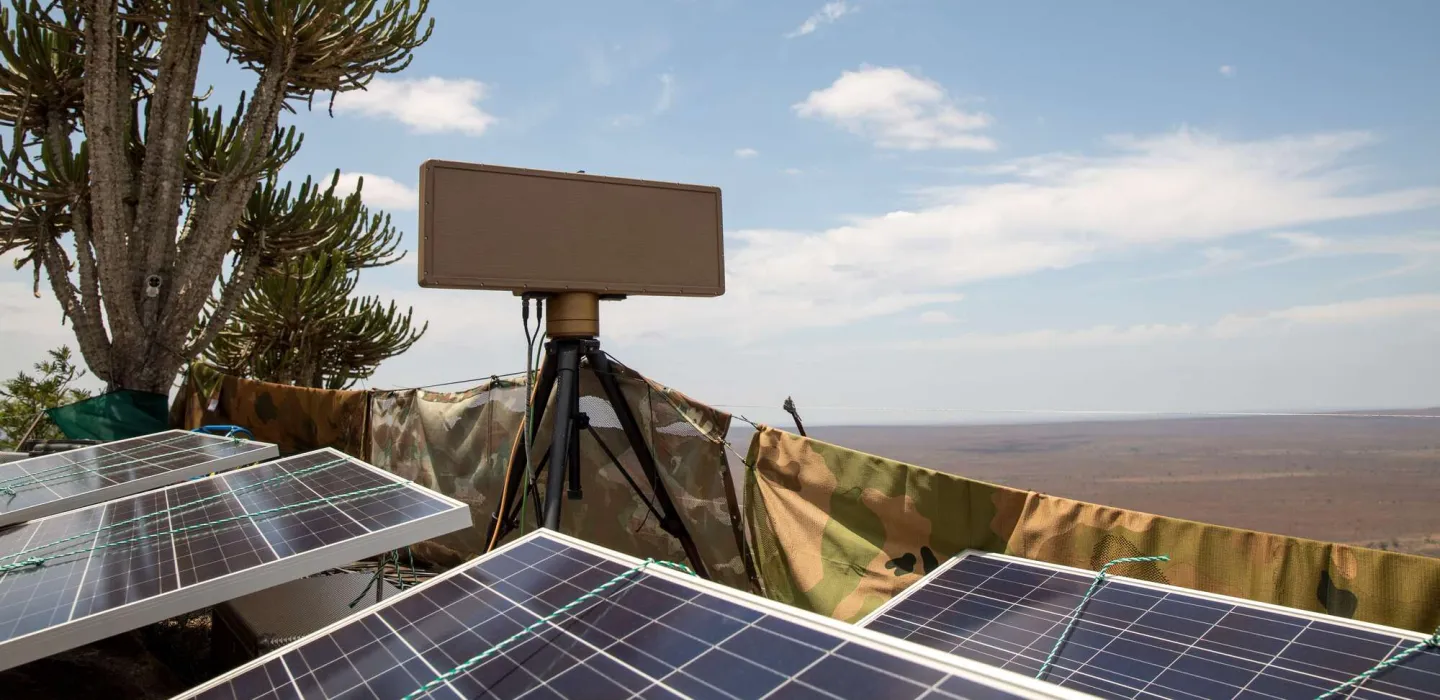
Radar-based system spots shots and shooters
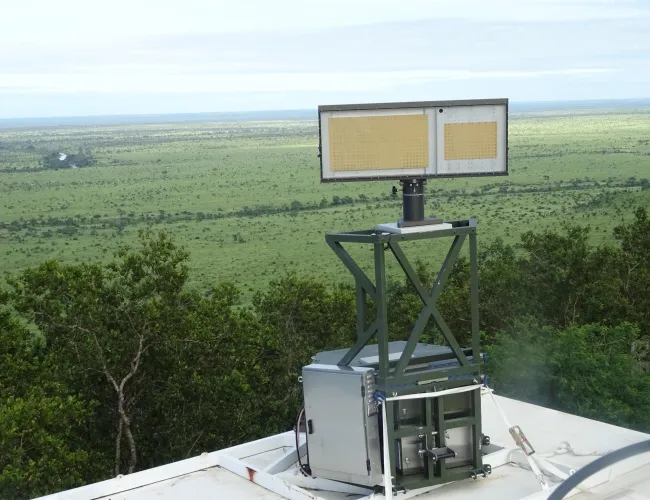
The CSIR has developed a real-time hostile fire indication sensor that alerts helicopter pilots and crew when they are under fired and identifies the shooter’s location – enabling immediate evasive or reactive tactics. The radar solution detects bullets passing within a 50 m radius of the helicopter, creating a protective warning ‘bubble’ around the aircraft. The system is currently at the commercialisation phase and is seeking interest from a local partner.
Offerings
Our research
Our facilities and tools